By P. Pedersen
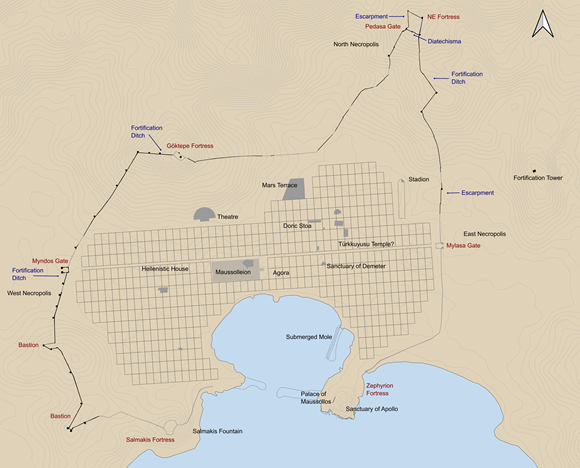 Fig. 1. Plan of Halikarnassos with the fortification system indicated (N. Bargfeldt and F.S. Nielsen).
Fig. 1. Plan of Halikarnassos with the fortification system indicated (N. Bargfeldt and F.S. Nielsen).
The Hekatomnid city wall of Halikarnassos is a very impressive monument of more than 7 kms in length and to-day it can be followed on far the largest part of its trace. It is a true “Geländemauer”, which included all the important heights in the outskirts of the ancient city-area (fig. 2). It introduces a long range of impressive Asia Minor city-walls of Late Classical and Hellenistic date. Certain technical details as the “double corner bond” (fig. 3) was apparently invented by the craftsmen of Maussollos and this feature can be followed in almost all Asia Minor fortifications until about the mid 2nd century BC, including Myndos, Theangela, Alinda, Alabanda, Latmos, Herakleia, Knidos, Kaunos, Labraunda, Ephesos, Samos, Pergamon and Assos as well as number of fortresses and watch-towers.
 Fig. 2. View over the city from the north-east with the remains of the city wall in the landscape (P. Pedersen).
Fig. 2. View over the city from the north-east with the remains of the city wall in the landscape (P. Pedersen).
Myndos Gate
The most impressive part of the city wall is the western gate complex called the Myndos Gate or the Tripylon. It was excavated and partly restored in 1998-2000 by Turkish archaeologists and architects with the participation of a Danish team from the University of Southern Denmark under the direction of Bodrum Museum.
 Fig. 3. Myndos Gate and the fortification ditch from the south (P. Pedersen).
Fig. 3. Myndos Gate and the fortification ditch from the south (P. Pedersen).
 Fig. 4. Myndos Gate south tower (P. Pedersen).
Fig. 4. Myndos Gate south tower (P. Pedersen).
 Fig. 5. Plan of the Myndos Gate area (P. Pedersen).
Fig. 5. Plan of the Myndos Gate area (P. Pedersen).
Fortification System
The masonry style of the city wall changes very much according to the character of the building stone, which was mostly quarried close to the wall except for some particularly important towers.
The wall was strengthened be a large number of towers and by a fortification ditch or – if on steeper slopes – an escarpment running 5-10 m in front of the wall. No less than 4 separate fortified strongholds or fortresses were included in the circuit.
 Fig. 6. View of the east side of the NE Extension from the north. The depression in front of the wall likely indicates a fortification ditch (P. Pedersen).
Fig. 6. View of the east side of the NE Extension from the north. The depression in front of the wall likely indicates a fortification ditch (P. Pedersen).
In spite of the great variation in masonry-style it is believed that the remains seen to-day are in all essentials remains of the wall constructed by Maussollos about 370 BC and besieged by Alexander in 334 BC. The siege of Halikarnassos by the troops of Alexander is recorded in detail by Arrian (Anab. I. 20-3) and Diodorus (Diod. 17. 24-7), which constitutes extremely important evidence for the city wall of Halikarnassos as well as on warfare and siege on the transition from Late Classical to Hellenistic times.
The innovative character of the fortification building by the architects of Maussollos and the long lasting influence of their work in Asia Minor fortification building seems to form an interesting parallel to the Ionian Renaissance in temples and monumental representative architecture.
Literature
Literature and Preliminary Reports
Pedersen P. 1994: The Fortifications of Halikarnassos, REA 96, 215-35.
McNicoll, A.W. 1997: Hellenistic Fortifications from the Aegean to the Euphrates, Oxford.
Pimouguet-Pedarros, I. 2000: Archéologie de la Défense. Histoire des fortifications antiques de Carie, - Époques classique et hellenistique, Paris.
Pedersen, P. 2011: The City Wall of Halikarnassos, in R. van Bremen & J.-M. Carbon (eds.), Hellenistic Karia. Proceedings of the First International Conference on Hellenistic Karia, Oxford 29 June – 2 July 2006, Talence, 269-316.
Pedersen, P. & U. Ruppe 2016: The Fortifications at Halikarnassos and Priene – some regional characteristics? in R. Frederiksen, S. Müth, P.I. Schneider & Mike Schnelle (eds.), Focus on Fortifications: New Research on Fortifications in the Ancient Mediterranean and the Near East. Monographs of the Danish Institute at Athens, Vol. 18. Oxford, 560-580.
Pedersen, P. 2023: The Outer Defenses of the City Wall of Halikarnassos – Ditches and Escarpments, in A. Diler & S. Özen (eds), Befestigungsbauten im westlichen Kleinasien. Fortifications in western Anatolia, Saarbrücken, 121-138.
In Danish
Carstens, A.M. & P. Pedersen 1999: Porten til Halikarnassos, Sfinx.